- Let x and y be elements of a normed linear vector space.
- Determine whether the following are valid inner products for the
indicated space.
- ⟨x,y⟩ = xT Ay, where A is a nonsingular,NxN matrix and x, y are elements of the space of N-dimensional vectors.
- ⟨x,y⟩ = xyT , where x and y are elements of the space of N-dimensional (column!) vectors.
- ⟨x,y⟩ = ∫ 0T x(t)y(T-t)dt, where x and y are finite energy signals defined over [0,T].
- ⟨x,y⟩ = ∫ 0T w(t)x(t)y(t)dt, where x and y are finite energy signals defined over [0,T] and w(t) is a non-negative function.
- E[XY ], where X and Y are real-valued random variables having finite mean-square values.
- Cov(X,Y ), the covariance of the real-valued random variables X and Y . Assume that X and Y have finite mean-square values.
- Under what conditions is
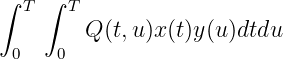
a valid inner product for the space of finite-energy functions defined over [0,T]?
- Determine whether the following are valid inner products for the
indicated space.
- Let x(t) be a signal of finite energy over the interval [0,T]. In other
words, x(t) is a vector in the Hilbert space L2(0,T). Signals
may be complex values, so that the appropriate inner product
is
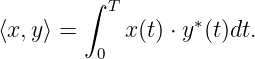
Consider subspace
 of L2(0,T) that consists of signals of the
form
of L2(0,T) that consists of signals of the
form
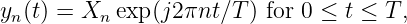
where Xn may be complex valued.
- Find the signal ŷn(t) that best approximates the signal x(t),
i.e., ŷn(t) minimizes ∥x - yn∥ among all elements of
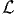 .
.
Hint: Find the best complex amplitude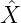 n.
n.
- Now define the error signal z(t) = x(t) -ŷn(t). Show that
z(t) is orthogonal to the subspace
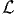 , i.e., it is orthogonal to
all elements of
, i.e., it is orthogonal to
all elements of 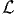 .
.
- How do the above results illustrate the projection theorem?
- Find the signal ŷn(t) that best approximates the signal x(t),
i.e., ŷn(t) minimizes ∥x - yn∥ among all elements of
- Linear Regression
The elements of a vector of random variables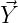 follow the
model
follow the
model
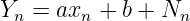
where xn are known and Nn are zero mean, iid Gaussian noise samples with variance σ2. The parameters a and b are to be determined. We can think of the solution to this problem as the projection of
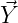 onto the
subspace spanned by a
onto the
subspace spanned by a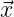 + b
+ b
- Determine the least-squares estimates for a and b, i.e., find
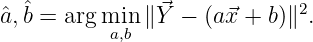
- What are the expected values of these estimates, E[â] and
E[
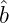 ]?
]?
- Compute â and
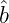 , when data are given by the (xn,Y n) pairs
, when data are given by the (xn,Y n) pairs
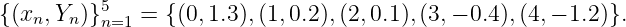
- Is it true that the least-squares estimates for a and b are given
by the inner products
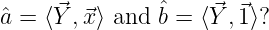
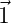 denotes a vector of 1’s. Explain why or why not?
denotes a vector of 1’s. Explain why or why not?
- Determine the least-squares estimates for a and b, i.e., find