


Next: Single Sideband Modulation
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Binary Transmission in the
The following three signals are used to construct a signal set for
transmission eight equally likely signals over an additive white Gaussian noise
channel with spectral height 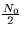 :
:
Specifically, the eight signals are constructed as linear combinations of the
three signals above:
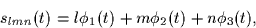
where each of l, m, and n can be either equal to zero or one.
- 1.
- Sketch and accurately label all eight possible signals.
- 2.
- Draw and accurately label a block-diagram of the receiver which minimizes
the probability of error for this signal set.
- 3.
- Draw and accurately label the the signal set in an appropriately chosen
signal space. Indicate the decision boundaries and state clearly which basis
functions span your signal space.
- 4.
- Find the probability of error the optimum receiver achieves with this
signal set.
- 5.
- Give a different signal set which achieves the same probability of error
as the signal set above.
Prof. Bernd-Peter Paris
3/3/1998
![\begin{picture}
(590,136)(20,660)
\setlength {\unitlength}{0.01in}
%
\thickl...
...}}}
\put(595,730){\makebox(0,0)[lb]{\raisebox{0pt}[0pt][0pt]{$T$}}}\end{picture}](img31.gif)
![\begin{picture}
(590,136)(20,660)
\setlength {\unitlength}{0.01in}
%
\thickl...
...}}}
\put(595,730){\makebox(0,0)[lb]{\raisebox{0pt}[0pt][0pt]{$T$}}}\end{picture}](img31.gif)
![]()