


Next: Suboptimum Receiver
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Sampling Systems
The following two signals are used to transmit equally likely messages
over a channel with AWGN of spectral height 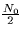 .
.
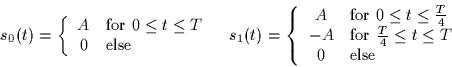
- 1.
- Sketch the simplest possible block diagram of the optimum receiver and
compute the probability of error attained by your receiver.
- 2.
- For the remainder of the problem, assume that the transmitted signal is
filtered by a linear filter with impulse response
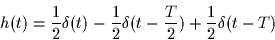
before the noise is added.
Such a channel model is appropriate to describe multi-path effects
in radio communication systems.
The following block diagram summarizes this channel.
Sketch the two possible received signals under the assumption that there is
no noise.
- 3.
- If the impulse response is unknown at the receiver, a reasonable approach
might be to continue to use the receiver from part (a)
which assumes that
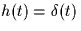 . Compute the probability of error that your receiver from part (a) achieves
if the actual channel impulse response h(t) is as given above
and the noise spectral height is
. Compute the probability of error that your receiver from part (a) achieves
if the actual channel impulse response h(t) is as given above
and the noise spectral height is
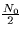 .
. - 4.
- If the channel impulse response h(t) is known at the receiver, can you design a
better receiver than the one in part (a)? If yes, draw a block diagram of the new
receiver and compute the associated probability of error. If no, explain why not.



Next: Suboptimum Receiver
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Sampling Systems
Prof. Bernd-Peter Paris
3/3/1998
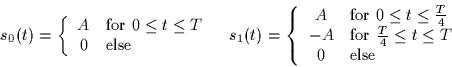
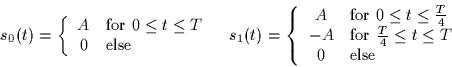
![]()
![\begin{picture}
(305,80)(45,720)
\setlength {\unitlength}{0.0125in}
%
\put(2...
...,800){\vector( 0, -1){ 47}}
\put(272,805){\makebox(0,0)[b]{$N_t$}}\end{picture}](img34.gif)