


Next: The Decryption Process
Up: EncryptionSeptember 30, 1997
Previous: EncryptionSeptember 30, 1997
- The process of encrypting a binary message is very simple.
- The binary message is simply xor'ed with another binary sequence.
- The second sequence should be random.
- Example: Let the message be ``ECE 101.''
- Using ASCII encoding, we get:
45x 43x 45x 20x 31x 30x 31x
- In binary form:
01000101 01000011 01000101 00100000 00110001 00110000 00110001
- Now select a random sequence of equal length, e.g.,
1010011 1000011 0101101 1101110 0110010 1010001 1101010
- The encrypted message is then:
| E |
C |
E |
SPACE |
1 |
0 |
1 |
| 45x |
43x |
45x |
20x |
31x |
30x |
31x |
| 1000101 |
1000011 |
1000101 |
0100000 |
0110001 |
0110000 |
0110001 |
| |
|
|
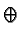 |
|
|
|
| 1010011 |
1000011 |
0101101 |
1101110 |
0110010 |
1010001 |
1101010 |
| |
|
|
= |
|
|
|
| 0010110 |
0000000 |
1101000 |
1001110 |
0000011 |
1100001 |
1011011 |
| 16x |
00x |
68x |
4Ex |
03x |
61x |
5Bx |
| SYN |
NULL |
h |
N |
ETX |
a |
[ |
- The encrypted message can now be transmitted and is meaningless to anyone
intercepting it.



Next: The Decryption Process
Up: EncryptionSeptember 30, 1997
Previous: EncryptionSeptember 30, 1997
Prof. Bernd-Peter Paris
1998-12-14