


Next: Electrical Error-Correction CodingSeptember 28,
Up: Coding in the non-Electrical
Previous: Computing the Check Digit
- The ASCII code is really a combined source and channel code.
- It provides for encoding of 128 characters.
-
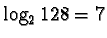 bits are required for that purpose.
bits are required for that purpose.
- The 8-th bit in an ASCII code word is used for error detection.
- An error detection scheme called parity checking is used.
- The term parity is used to indicate if the number of 1's in an
ASCII code word is even or odd.
- In a communication system, it is agreed between receiver and transmitter
if even parity or odd parity is to be used.
- If even parity is used the transmitter sets the 8-th bit of an ASCII word
such that there are 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8 occurences of 1's.
- Example:
- lower case a is encode as 61x (or 110 0001).
- By convention, bit 1 is on the rightand bit 7 is on the left.
- With even parity, a '1' is added on the left to yield 4 1's.
- Hence the codeword 1110 0001 would be transmitted for character 'a'.
- The receiver can determine that an error occured by checking the parity of
a received code word.
- Clearly, any error involving a single bit can be detected (but not
corrected).
- To recover from an error, the receiver would request retransmission of
erroneous code words.



Next: Electrical Error-Correction CodingSeptember 28,
Up: Coding in the non-Electrical
Previous: Computing the Check Digit
Prof. Bernd-Peter Paris
1998-12-14