


Next: Influence of Unknown Delays
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: On-Off-Keying
The following two signals are used to transmit equally likely messages
over a channel with AWGN of spectral height 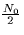 .
.
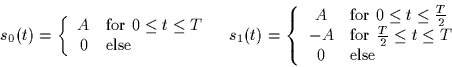
- 1.
- Sketch the simplest possible block diagram of the optimum receiver and
compute the probability of error attained by your receiver.
- 2.
- For the remainder of the problem, assume that the transmitted signal is
filtered by a linear filter with impulse response
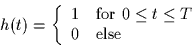
before the noise is added.
The following block diagram summarizes this channel.
Sketch the two possible received signals under the assumption that there is
no noise.
- 3.
- If the impulse response is unknown at the receiver, a reasonable approach
might be to continue to use the receiver from part (a)
which assumes that
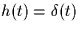 . Compute the probability of error that your receiver from part (a) achieves
if the actual channel impulse response h(t) is as given above
and the noise spectral height is
. Compute the probability of error that your receiver from part (a) achieves
if the actual channel impulse response h(t) is as given above
and the noise spectral height is
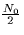 .
. - 4.
- If the channel impulse response h(t) is known at the receiver, can you
design a
better receiver than the one in part (a)? If yes, draw a block diagram of the
new
receiver and compute the associated probability of error. If no, explain why
not.



Next: Influence of Unknown Delays
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: On-Off-Keying
Prof. Bernd-Peter Paris
3/3/1998
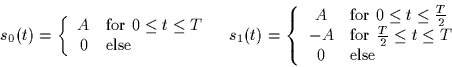
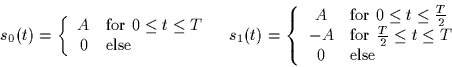
![]()
![\begin{picture}
(305,80)(45,720)
\setlength {\unitlength}{0.0125in}
%
\put(2...
...,800){\vector( 0, -1){ 47}}
\put(272,805){\makebox(0,0)[b]{$N_t$}}\end{picture}](img48.gif)