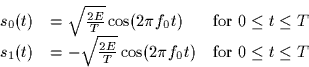Next: AM Stereo Signals
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Binary Signal Sets
A BPSK signal set is used to transmit equally likely signals over a channel
which adds white Gaussian noise (autocorelation function 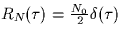 to the transmitted signal. Hence, the signal set
consists of the signals
to the transmitted signal. Hence, the signal set
consists of the signals
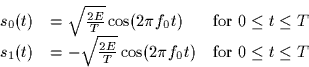
You may assume that f0T is an integer.
- 1.
- Sketch a block diagram of a receiver which minimizes the probability of
error and uses a single (matched) filter followed by a sampler.
Sketch the impulse response of the matched filter used in yor detector.
- 2.
- Compute the probability of error your receiver achieves.
- 3.
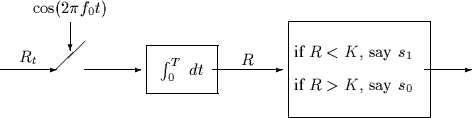
- To save some expenses, the following receiver is considered.
The switch in the receiver above is closed whenever
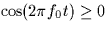 and is open when
and is open when 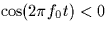 .
.
Find the distribution of the random variable R for both cases, s0(t) was
transmitted and s1(t) was transmitted.
- 4.
- Find the value of the threshold K which minimizes the probability of
error.
- 5.
- What is the minimum probability of error achievable with the receiver
shown above?
Prof. Bernd-Peter Paris
3/3/1998
![]() to the transmitted signal. Hence, the signal set
consists of the signals
to the transmitted signal. Hence, the signal set
consists of the signals