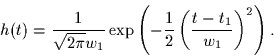Next: Pulse Position Modulation
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Influence of Phase Errors
- 1.
- Show that the Fourier transform of the signal
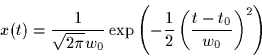
is given by
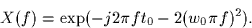
- 2.
- Let x(t) be the input to a linear system with impulse response
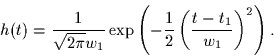
Find the resulting output signal y(t).
- 3.
- Is the linear system in part (b) causal? Explain.
- 4.
- Now let x(t) be input to a linear system with impulse response
h(t) = u(t) where u(t) denotes the unit step function.
(I.e., u(t)=1 for
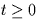 and u(t)=0 for t < 0).
Find the resulting output signal.
and u(t)=0 for t < 0).
Find the resulting output signal.
Hint: One of parts (b) and (d) is best solved in the frequency domain while
the other is easier in the time domain.
Prof. Bernd-Peter Paris
3/3/1998
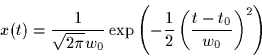
![]()
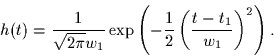
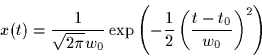
![]()