


Next: M-ary Signal Sets
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Problem 14
The following binary signal set is used to transmit equally likely
messages over an additive white Gaussian noise channel (spectral
height 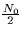 ),
),
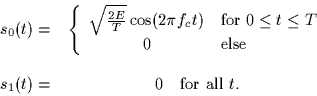
- 1.
- Draw a block diagram of the optimum receiver and compute the
probability of error for this receiver.
- 2.
- Assume now that the signal s0(t) experiences a phase shift
during transmission, i.e., if s0(t) is transmitted the received
signal is
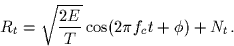
Compute the probability of error that your receiver from part (a)
achieves in this situation.
- 3.
- If the phase error is large, the performance of the coherent
receiver is unacceptable.
Draw a block diagram of a receiver that performs well for
all values of
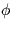 .
. - 4.
- If it is known that the phase error is small, i.e.,
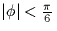 , which receiver performs better: the coherent receiver
from part (a) or the non-coherent receiver from part (c). Explain.
, which receiver performs better: the coherent receiver
from part (a) or the non-coherent receiver from part (c). Explain.
Hint: 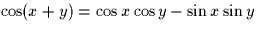 .
.
Prof. Bernd-Peter Paris
3/3/1998
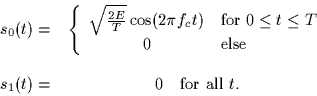
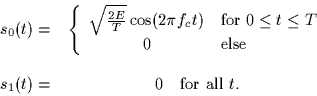
![]()