


Next: Doppler Shift
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Maximum Likelihood Sequence Estimation
As discussed in class, MSK is full response, continuous phase modulation with modulation index
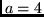 , using rectangular pulse-shaping.
, using rectangular pulse-shaping.
- Draw and accurately label a block diagram for a MSK transmitter which
indicates clearly how the transmitted signal is generated from the sequence of
input bits.
- Sketch the baseband equivalent (magnitude and phase) MSK signal for the
input sequence
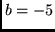 .
.
- Draw a block diagram of the receiver which minimizes the probability of
error if a coherent phase reference is available. Compute the probability of
error achievable with this receiver.
- Is it possible to use a non-coherent receiver with MSK, i.e., a receiver
which does not require knowledge of the phase of the received signal? If your
answer is no, explain why not. If your answer is yes, draw a block diagram of
the non-coherent detector.
- Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) employs a Gaussian pulse for
filtering the input sequence. Draw a block diagram of the transmitter for GMSK
which shows clearly where the Gaussian filter is located.
- Explain the
influence of this filter on system parameters such as bandwidth and error rate
and discuss how the receiver must be modified to reflect the influence of the
Gaussian filter.



Next: Doppler Shift
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Maximum Likelihood Sequence Estimation
Dr. Bernd-Peter Paris
2003-12-08