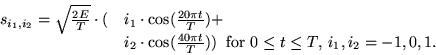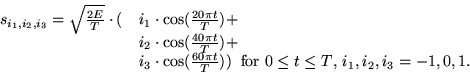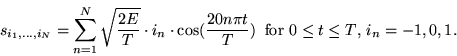Next: Multi-Path Channels
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Imperfect Phase Information
The following signal set is used to transmit equally likely messages
over an additive white Gaussian noise channel with spectral height
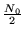 ,
,
Thus, this signal set consists of 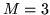 signals.
signals.
- Draw and accurately label a block diagram for the optimum
receiver for this signal set.
- Draw and accurately label the signal constellation in an
appropriately chosen signal space and indicate the decision
boundaries formed by the optimum receiver.
Then, compute the probability of error achieved by the optimum
receiver.
- Repeat part (b) for the following signal set
- Repeat part (b) for the following signal set
- Derive a general expression for the probability of error of the
N-dimensional signal set
Dr. Bernd-Peter Paris
2003-01-28