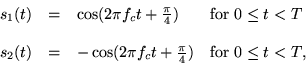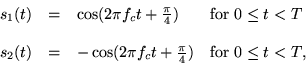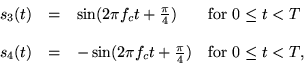Next: Imperfect Phase Information
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Diversity Reception
The signal set
where 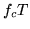 is an integer,
is used to transmit one of two equally-likely messages over an
additive, white Gaussian noise channel with spectral height
is an integer,
is used to transmit one of two equally-likely messages over an
additive, white Gaussian noise channel with spectral height
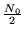 .
.
- Draw a block diagram of the optimum receiver.
Can this receiver be implemented using only one correlator.
- Compute the probability of error for this receiver.
- Now, the signals
are added to the above signal set. Each signal is then used to transmit one
of four equally likely messages. Draw a block diagram of the optimum
receiver for this quaternary signal set in additive white
Gaussian noise.
- Compute the resulting probability of error.
Hint: Remember that the likelihood ratio test
can also be written as
Dr. Bernd-Peter Paris
2003-01-28