


Next: Binary Signaling over a
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Binary Signal Sets
In some situations, it is advantageous to hide the presence of a communication
system. The following signaling scheme accomplishes that objective.
The binary communications system under consideration uses the following signals
to transmit equally likely messages over an additive, white Gaussian noise
channel (spectral height 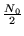 )
)
where 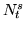 is a zero-mean, white Gaussian noise process with autocorrelation
function
is a zero-mean, white Gaussian noise process with autocorrelation
function
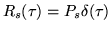 .
.
Assume first that the following receiver front-end is being used, where
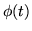 denotes an arbitrary signal of unit energy, i.e.,
denotes an arbitrary signal of unit energy, i.e.,
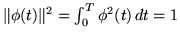 .
.
- Compute the conditional distribution of the random variable
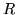 for each
of the two signals
for each
of the two signals 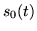 and
and 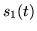 .
.
- Assume now that the conditional distributions for the random variable
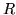 are given by
are given by
Find the likelihood-ratio test that minimizes the probability of
error. Simplify as much as possible.
- Find the probability of error for your test.
- Consider now the following receiver front-end
The functions 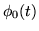 and
and 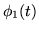 are orthonormal. Find the joint
distribution of random variables
are orthonormal. Find the joint
distribution of random variables  and
and 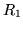 .
.
- For the receiver front-end above, devise the minimum probability of error
test for determining which of the
two signals
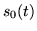 and
and 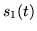 was transmitted. You do not have to compute
the probability of error for your test, but you must provide a convincing
argument if the probability of error will be larger or smaller than with the
first receiver front-end.
was transmitted. You do not have to compute
the probability of error for your test, but you must provide a convincing
argument if the probability of error will be larger or smaller than with the
first receiver front-end.
- What is the optimum receiver for this problem?



Next: Binary Signaling over a
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Binary Signal Sets
Dr. Bernd-Peter Paris
2003-01-28
![]() )
)
![]() denotes an arbitrary signal of unit energy, i.e.,
denotes an arbitrary signal of unit energy, i.e.,
![]() .
.
![\begin{picture}(60,30)
\setlength{\unitlength}{1mm} \put(0,10){\vector(1,0){12}...
...put(45,10){\vector(1,0){15}}
\put(52.5,11){\makebox(0,0)[b]{$R$}}
\end{picture}](img186.png)
![\begin{picture}(280,260)(40,530)
\setlength{\unitlength}{0.01in}%
% thicklines...
...,0)[b]{$\phi_0(t)$}}
\put(140,540){\makebox(0,0)[b]{$\phi_1(t)$}}
\end{picture}](img192.png)
![]() and
and ![]() are orthonormal. Find the joint
distribution of random variables
are orthonormal. Find the joint
distribution of random variables ![]() and
and ![]() .
.