Next: Problem 11
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Suboptimum Linear Receivers for
The following QAM-signal set is used to
transmit equally likely messages over an additive white Gaussian
noise channel with spectral height 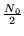 ,
,
Thus the signal set consists of 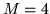 signals.
signals.
- Draw and accurately label the signal constellation in an
appropriately chosen signal space and indicate the decision
boundaries formed by the optimum receiver.
- Compute the probability of error achieved by the optimum
receiver.
- How many bits
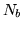 are sent with each transmission
for this signal set?
are sent with each transmission
for this signal set?
- Define the average bit-energy
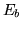 as
as
where 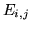 denotes the energy of signal
denotes the energy of signal 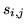 and
and
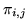 denotes the corresponding a priori probabilities.
Compute the average bit-energy
denotes the corresponding a priori probabilities.
Compute the average bit-energy 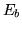 for this signal set.
for this signal set.
- Repeat parts (a)-(c) for the following signal set with
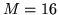 signals:
signals:
- If both signal sets would be using the same bit-energy
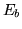 , which signal set
yields the smaller probability of error?
Explain.
, which signal set
yields the smaller probability of error?
Explain.
- Which other very important parameter in a communication system may lead a
system designer to choose the second signal set over the first signal set,
particularly if the signal-to-noise ratio is large? Explain.



Next: Problem 11
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Suboptimum Linear Receivers for
Dr. Bernd-Peter Paris
2003-01-28