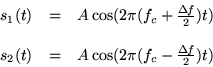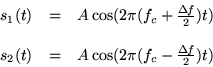Next: Binary Signal Sets
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Collected Problems
In a coherent FSK signalling scheme the signals 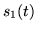 and
and 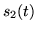 are defined to be
are defined to be
These signals are used to transmit equally-likely bits over a
channel which adds white Gaussian noise of spectral height
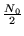 to the signal.
to the signal.
- Assuming
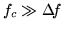 , show that the ``correlation
coefficient''
, show that the ``correlation
coefficient'' 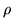 of the signals
of the signals 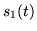 and
and 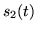 , defined as
, defined as
is given approximately by
where 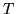 is the duration of a bit interval.
is the duration of a bit interval.
- What is the minimum value of the frequency shift
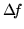 for which the signals are orthogonal?
for which the signals are orthogonal?
- Draw a block diagram of the receiver which attains the minimum
probability of error.
- Compute the minimum probability of error as a function of
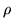 .
.
- What is the value of
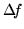 that minimizes the probability
of error?
that minimizes the probability
of error?
Hint: You may need these equations:



Next: Binary Signal Sets
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Collected Problems
Dr. Bernd-Peter Paris
2003-01-28