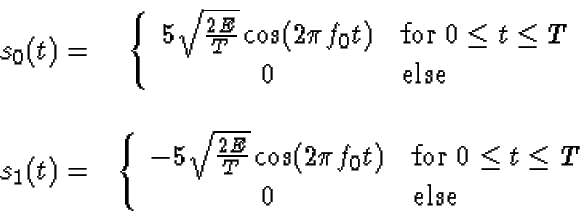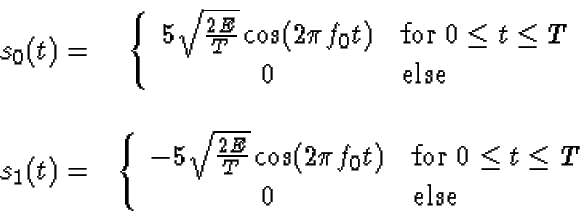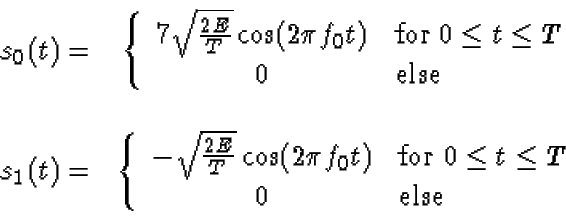Next: Suboptimum Receivers
Up: Collected Problems
Previous: Collected Problems
The following binary signal set is used to transmit equally likely
messages over an additive white Gaussian noise channel (spectral
height
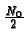 ),
),
- 1.
- Draw a block diagram of the optimum receiver.
- 2.
- Compute the
probability of error for this receiver.
- 3.
- Repeat parts (a) and (b) for the following signal set:
- 4.
- Sketch and accurately label a signal space diagram, including
decision boundaries, for each of the two signal sets above.
- 5.
- Verify that both of the above signal sets use the same average bit energy
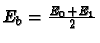 .
Then compare their performance with respect to the minimum probability
of error. Explain any differences. Which signal set do you prefer?
.
Then compare their performance with respect to the minimum probability
of error. Explain any differences. Which signal set do you prefer?
Prof. Bernd-Peter Paris
2002-04-22